Why Refuel
Do More With Your Spacecraft

It’s Time to Eliminate Single-Use Spacecraft
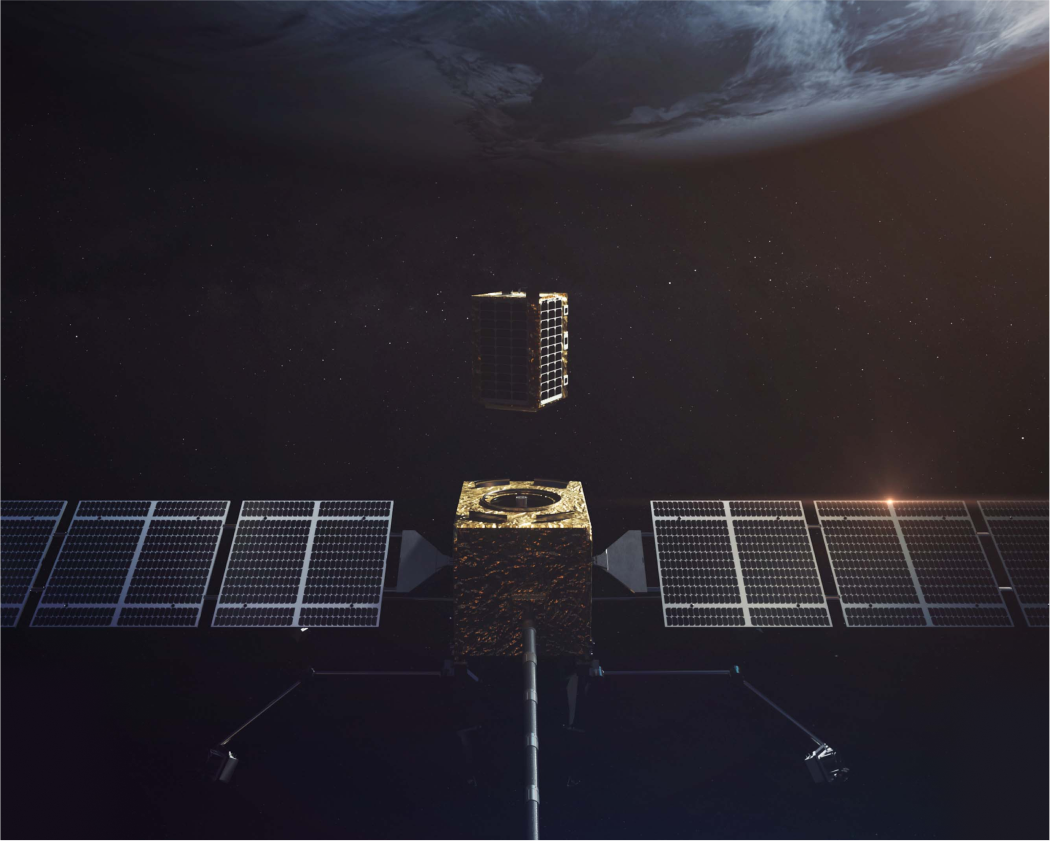

Nothing else is limited to one tank of fuel...
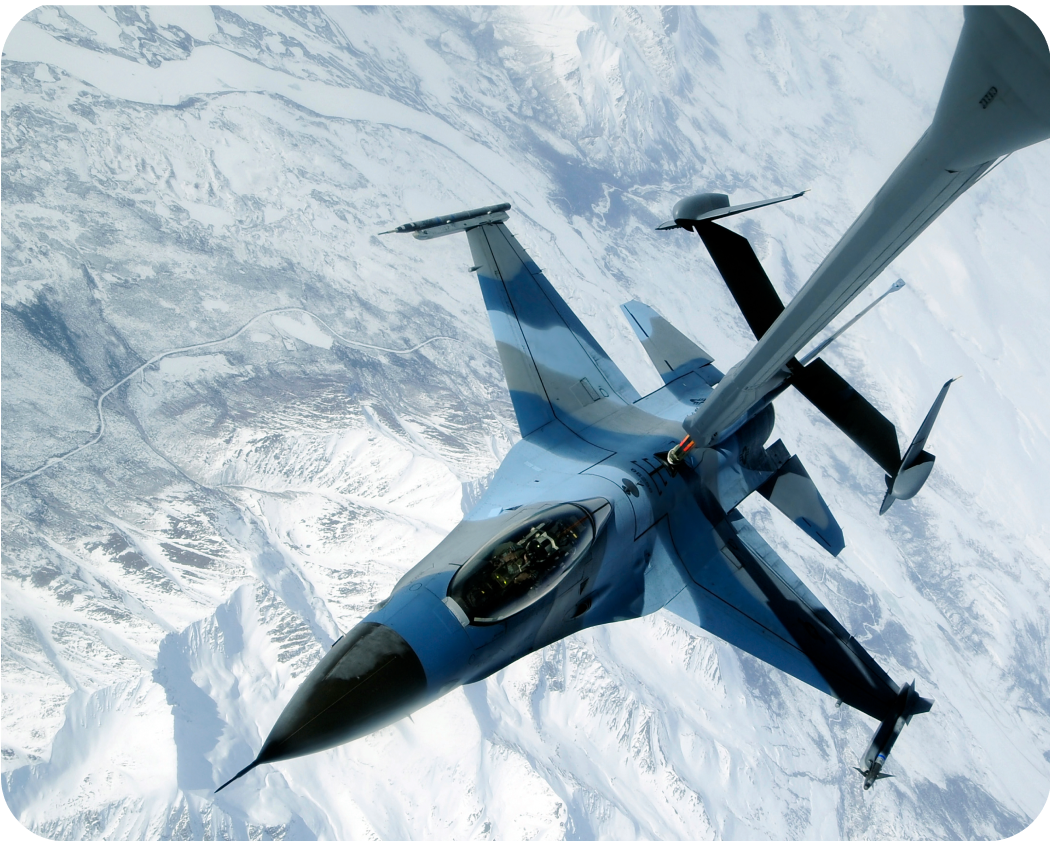

…cars, planes, boats, and even rockets refuel
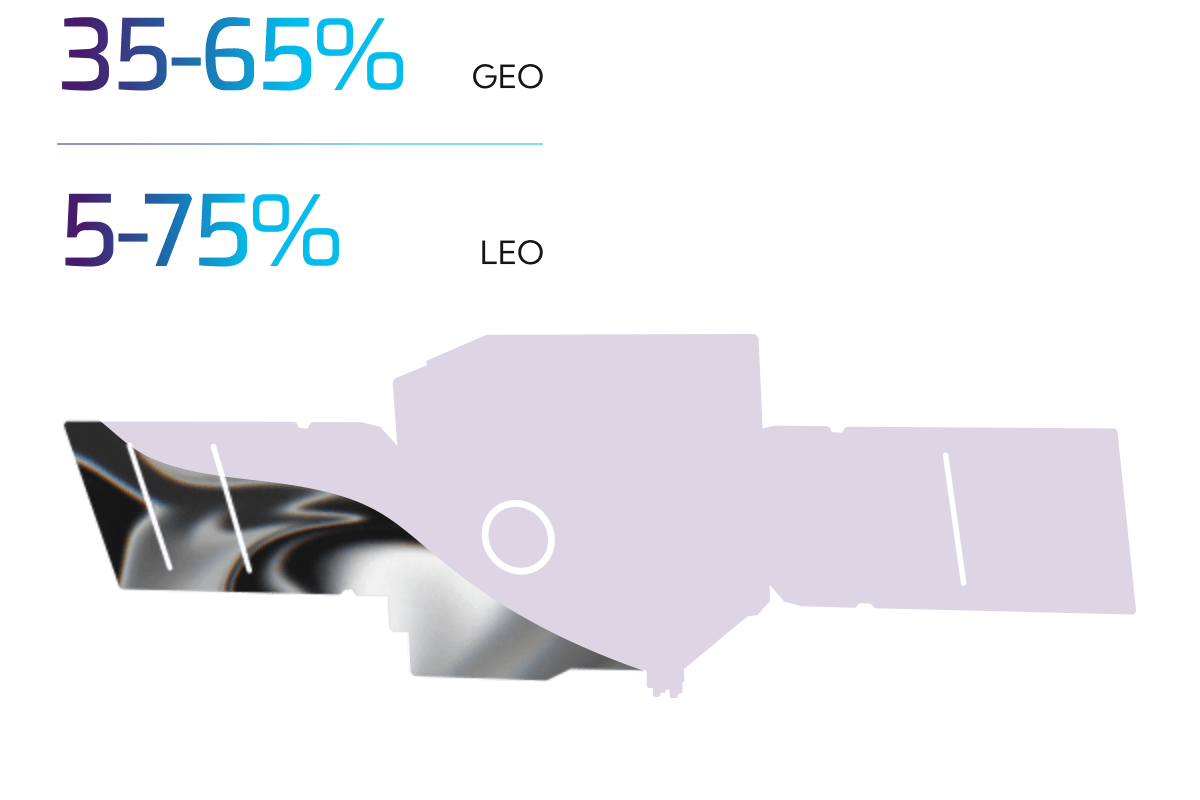
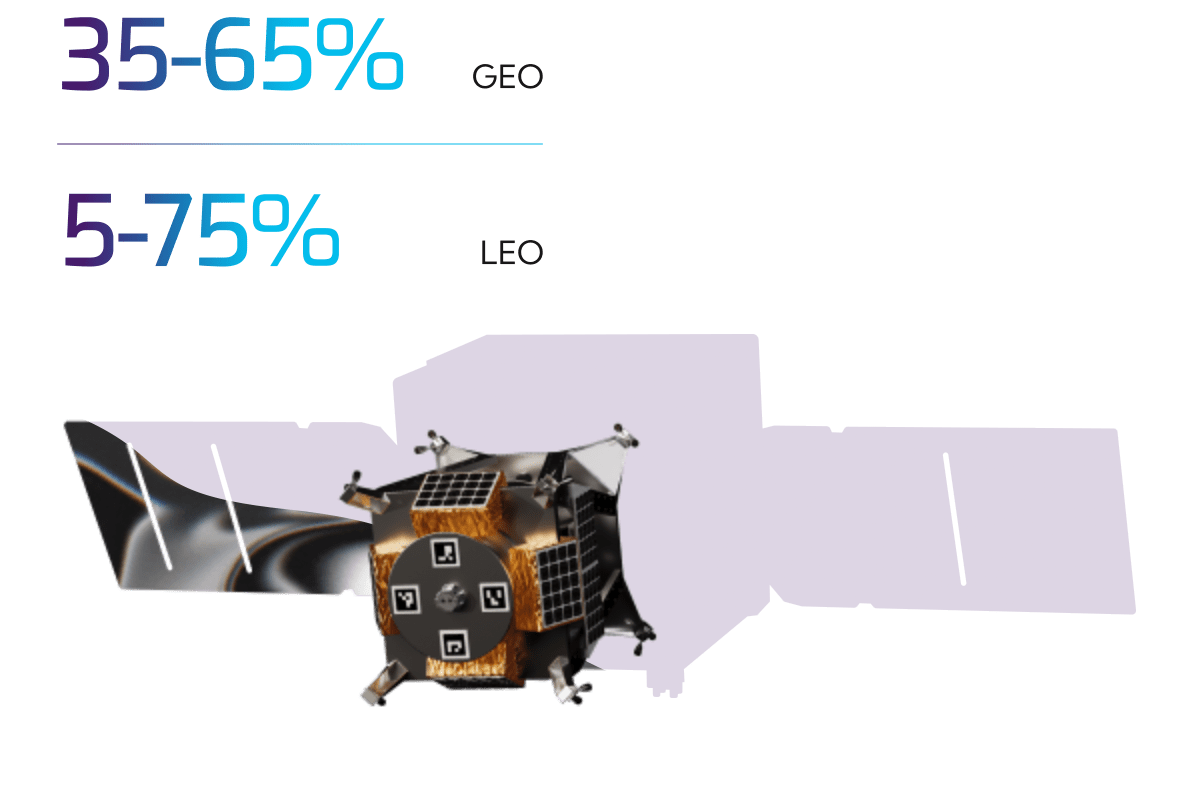
Satellites Dedicate up to 75% of Mass to Propellant
Propellant is needed for orbit insertion, raising, and maintenance,
as well as maneuvering and deorbiting.
When You Design for Refueling, You Free up Mass Budgets...
Trade fuel mass for payload mass,
or decrease launch costs
Get More From Your Missions...
Get to orbit faster,
do more while there
And Unlock Novel Business Models
Secure commercially
viable and sustainable businesses
Refueling Saves Billions in Replacement Costs
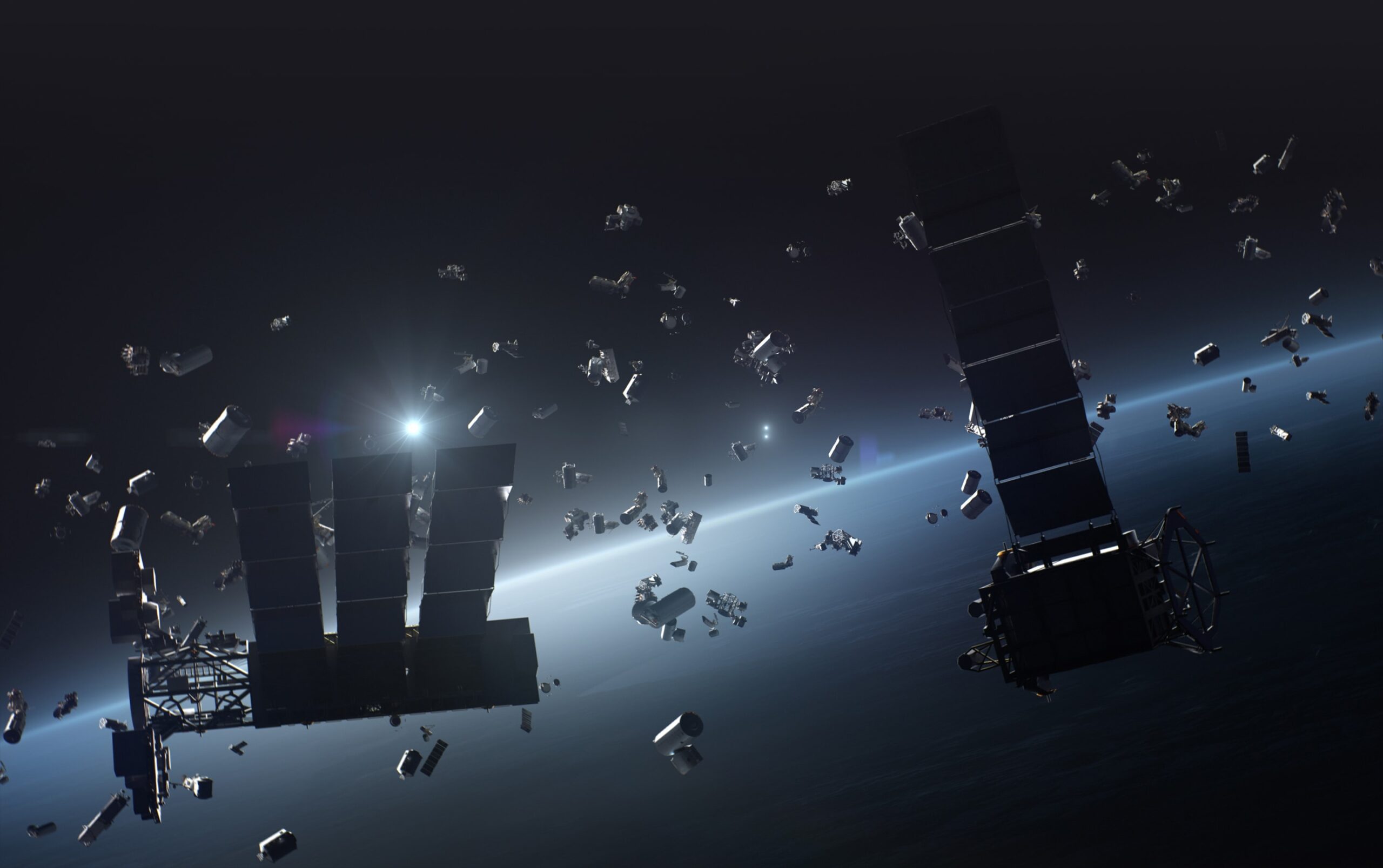

And Ensures Sustainable Operations, Minimizing Space Debris
When satellites run out of propellant, they either burn up in the atmosphere or are sent to a graveyard orbit. If they run out unexpectedly and cannot refuel, they become dangerous space debris.
What Could You Do
With More Delta-V?


Enhance Mobility
- Reposition assets
- Negate mission life reduction caused by collision avoidance maneuvers
- Enable on-demand retaking
- Correct orbital insertion inaccuracies


Increase Revenue Potential
- Extend spacecraft lifetime
- Trade fuel mass for payload mass
- Enable faster asset deployment
- Decrease launch cost



Enable New Business Models
- Perform secondary missions
- Offer unique capability to clients
- Enable access to novel maneuvers, orbits, spacecraft designs, and constellation architectures
Case Studies
-
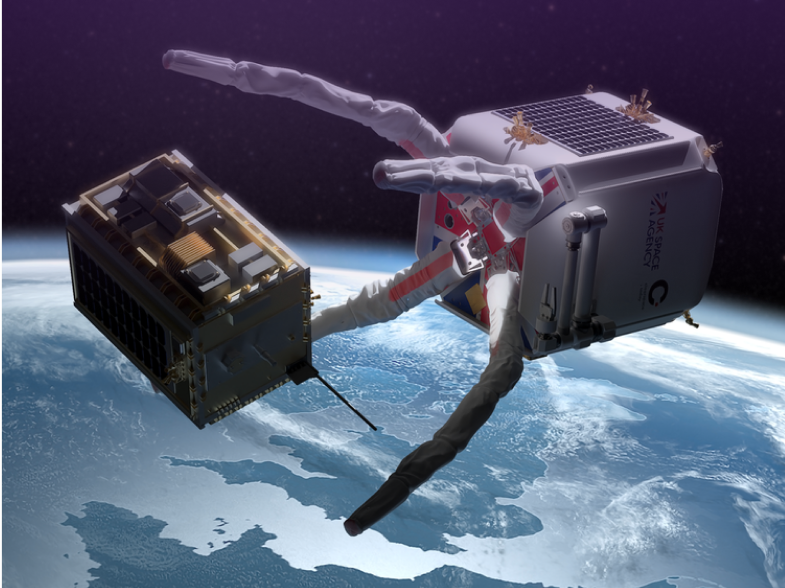


Large-Scale Economically Viable Debris Removal Enabled by Refueling
As Low Earth Orbit (LEO) sees ever increasing debris congestion, sustainable solutions to debris mitigation…
Read more -
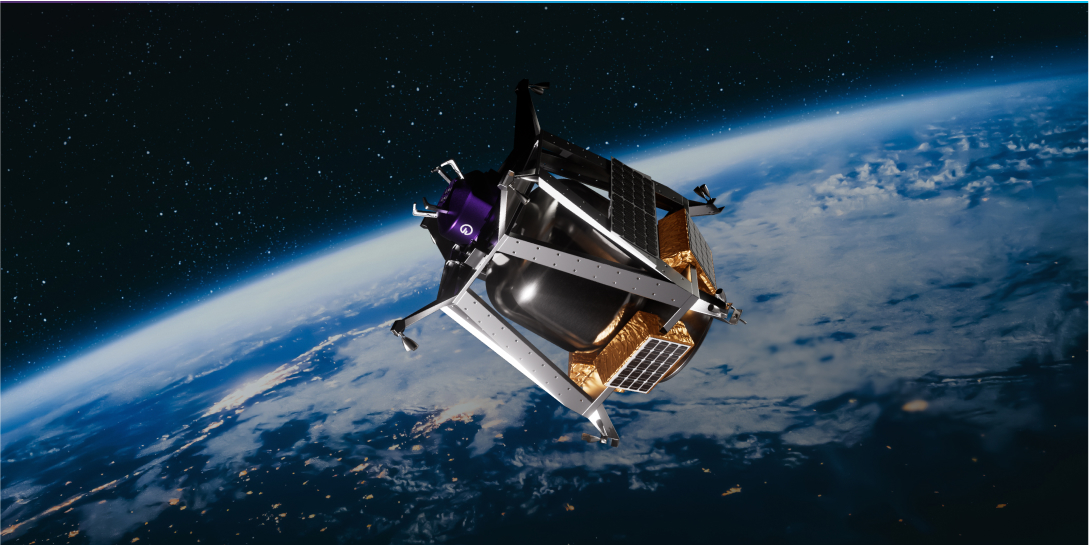


Refueling Architectures for VLEO Missions
Missions to very low Earth orbit (VLEO) require large supplies of propellant to maintain their…
Read more -
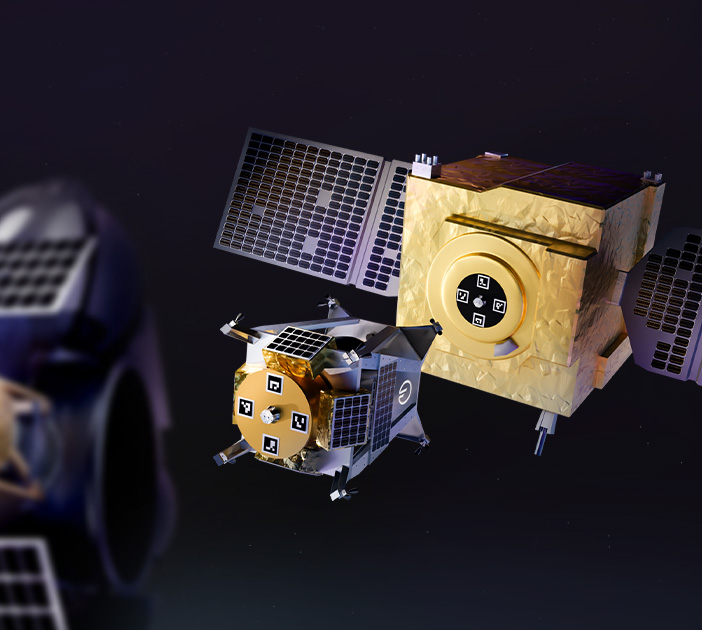


Operational Flexibility and Asset Retasking Enabled by In-Space Refueling
Refueling offers more than just mission life extension. By freeing missions from the constraints of…
Read more

!["The €1-billion (US$1.2-billion) mission [ESA Gaia] is set to take data until 2024, when its fuel is expected to run out."](https://www.orbitfab.com/wp-content/uploads/NatureArticle.jpg)